Back to: Multiplier Event Luxembourg

NeoPixel #9
The NeoPixel #9 is used to distinguish between a good reading and the request for a new attempt.
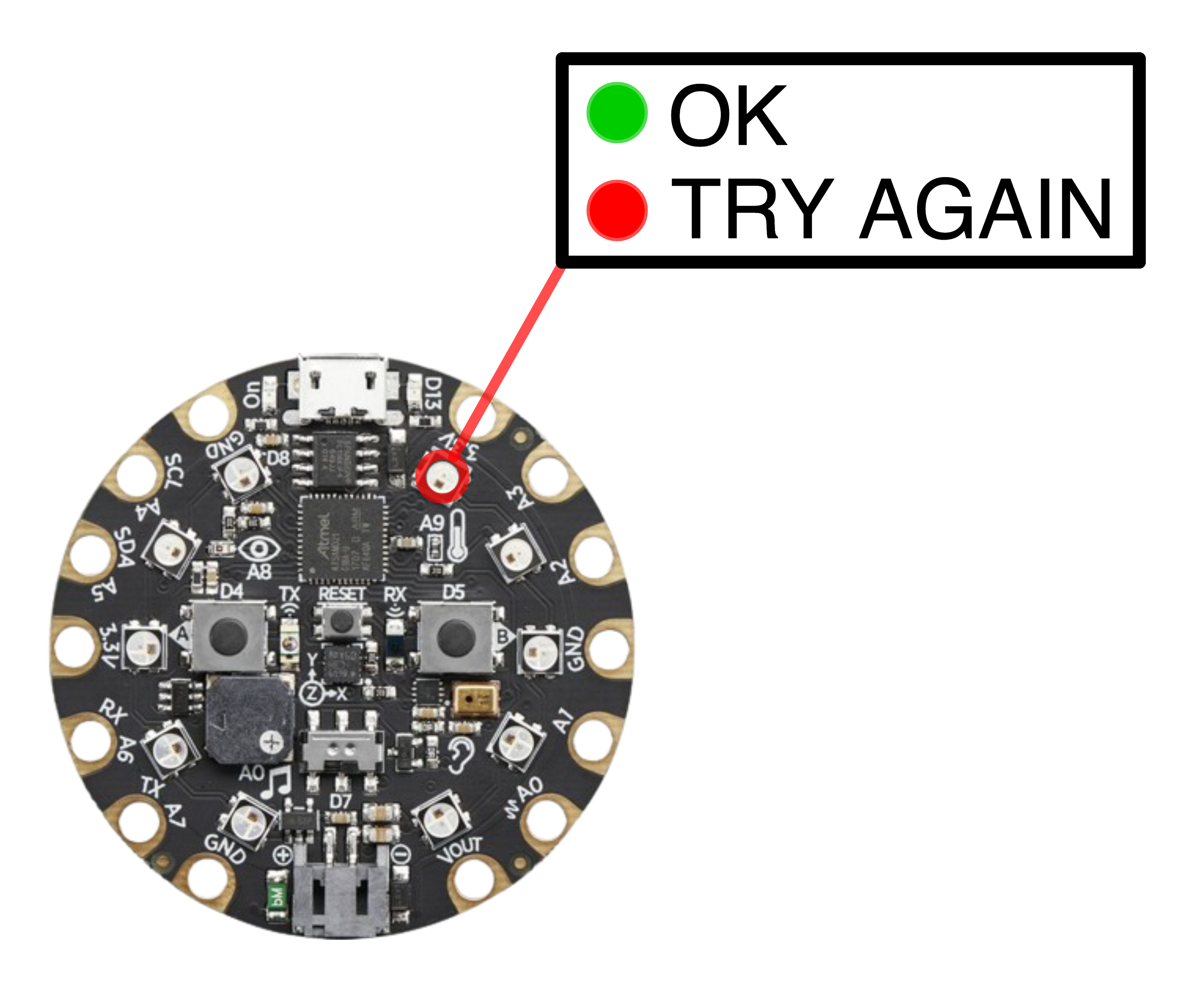
# NeoPixel #9 is set to red to indicate no (good) reading. cp.pixels[9] = (255, 0, 0)
# NeoPixel #9 is set to indicate the quality of the reading.
if reading:
cp.pixels[9] = (0, 255, 0) # Green light for good reading.
else:
cp.pixels[9] = (255, 0, 0) # Red light for try again.
continue
NeoPixel #8
The NeoPixel #8 is used to indicate the sign of the angle \(\alpha\). When measuring a tree, the angle will always be positive. If one were measuring downwards from a bridge, the angle would be negative.
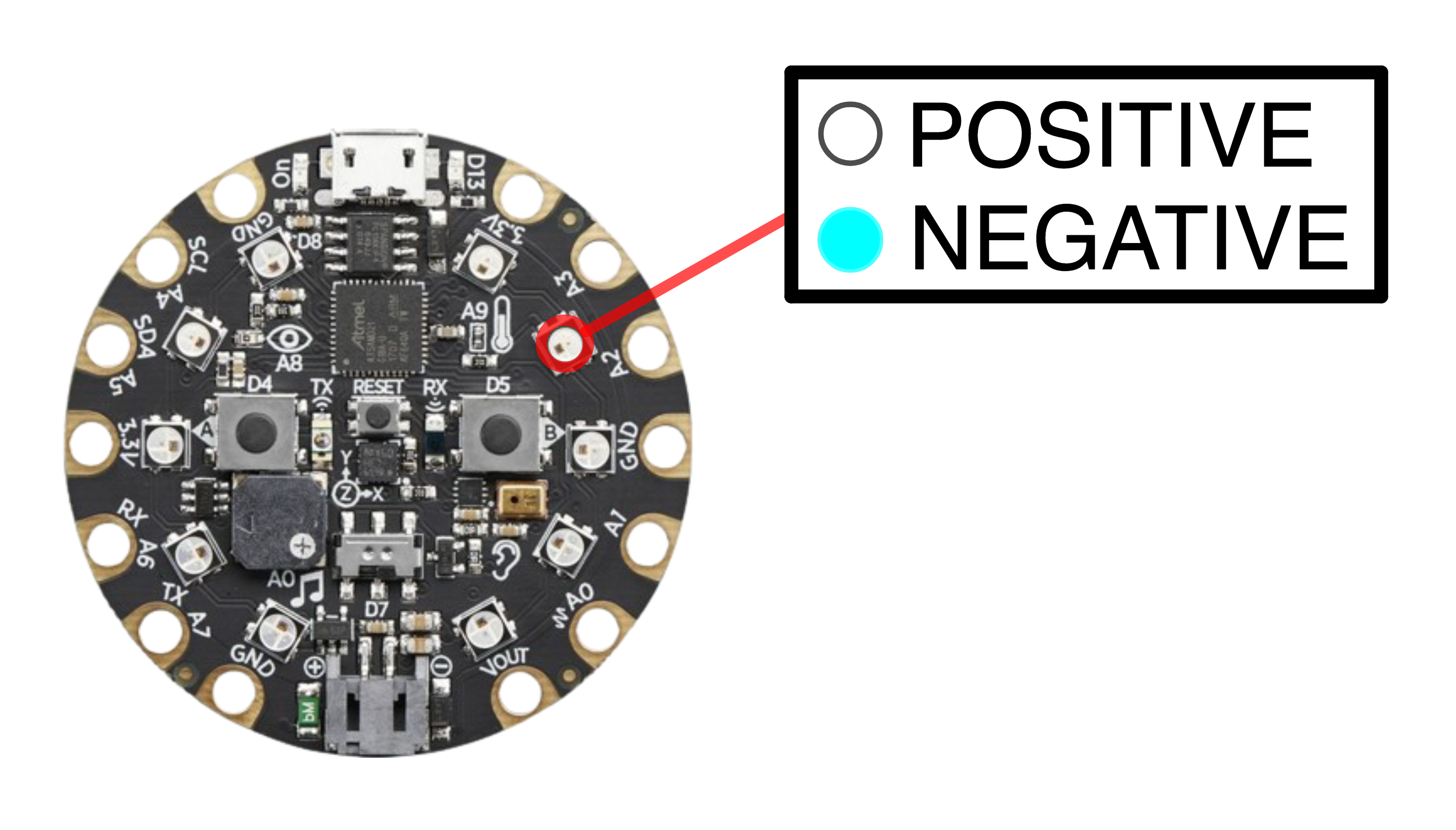
# NeoPixel #8 is set to indicate the sign of the angle.
if tan_alpha < 0:
cp.pixels[8] = (0, 0, 255) # Blue light for negative.
else:
cp.pixels[8] = (255, 255, 255) # White light for positive.
NeoPixel #0 to #7
The first eight NeoPixels will indicate the magnitude of the angle \(\alpha\) in degrees as 8-bit number. To get this magnitude, the light-up digits need to be summed up.
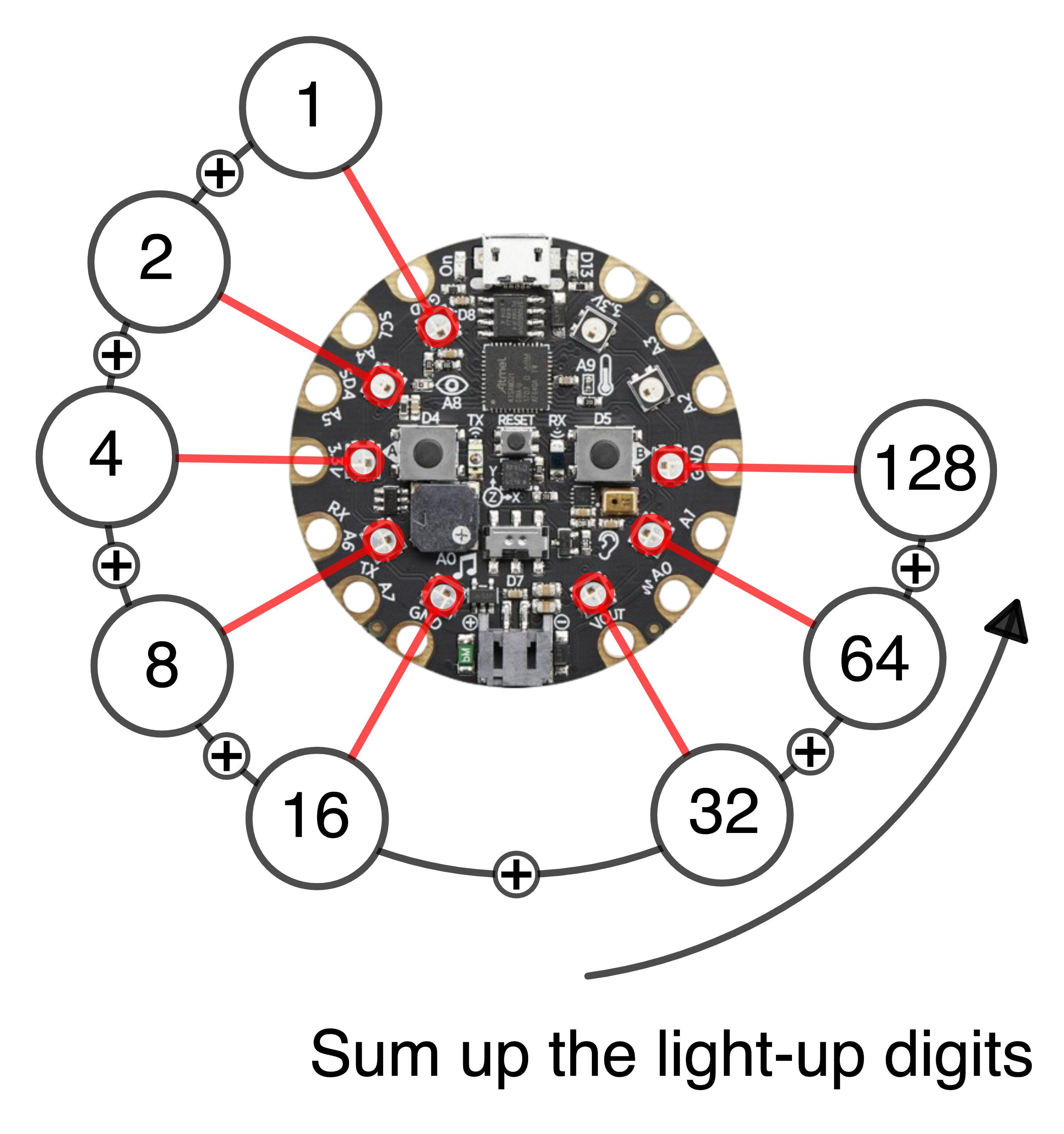
# Display angle magnitude on NeoPixels #0 to #7 as 8-bit value.
for p in range(8):
# Check if right bit (0x1 = 00000001) is set.
if alpha & 0x1 == 1:
cp.pixels[p] = (255, 255, 255) # Turn on the NeoPixel
else:
cp.pixels[p] = (0, 0, 0) # Turn off the NeoPixel
# Shift 𝛼 right by 1 bit.
# Dropping the right bit equals dividing the number by 2.
alpha = alpha >> 1
Slide Switch
Depending on the slide switch, the Circuit Playground Express board will write to
- the serial console if the switch is towards the left, or
- the CircuitPython storage if the switch is towards the right.
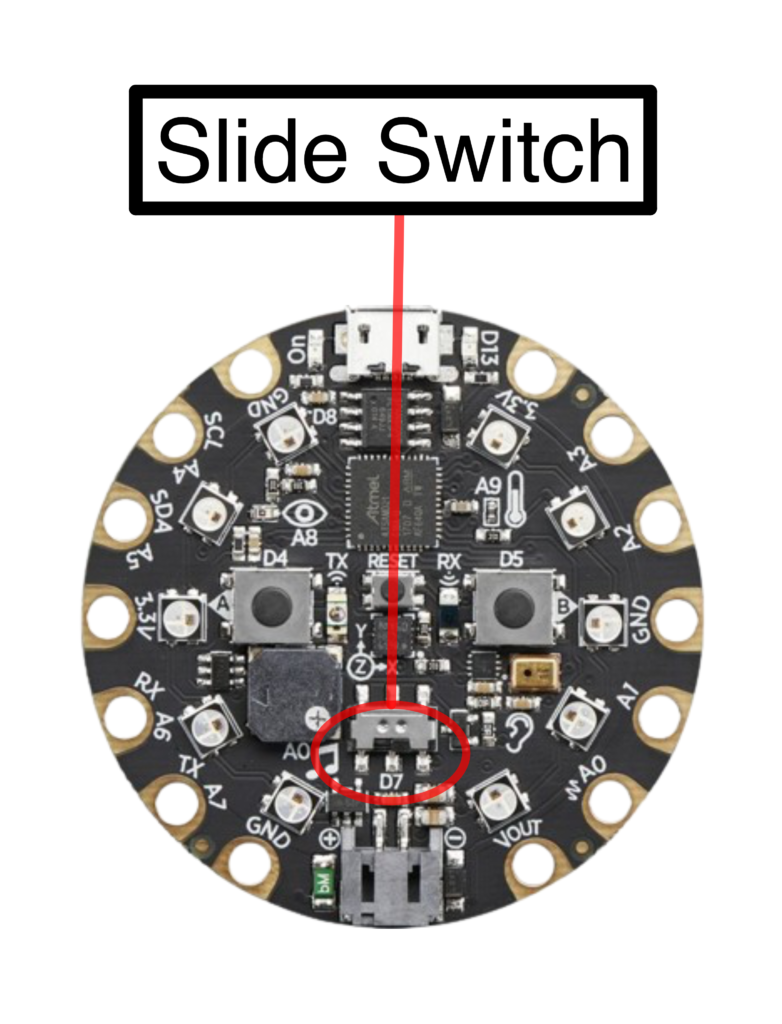
# Depending on the switch, write to
# * the serial console (if True, i.e. left), or to
# * the CircuitPython storage (if False, i.e. right).
if cp.switch:
# Read d and e as float.
d = float(input("What is the distance to the object in meters? "))
e = float(input("What is the eye level in meters? "))
# Substract e if tan_alpha is negative.
e = math.copysign(e, tan_alpha)
# Print the height of the object.
print("The height of the object is", "{:.2f}".format(d * tan_alpha + e), "meters.\n")
else:
f = open("tan_alpha.csv", "a")
f.write(repr(tan_alpha) + "\n")
f.close()





